
Nous vivrons. Et nous guérirons. Les cicatrices... Nous les gardons. Pour ne pas oublier.
After an overwhelming battle against the rats, it is time for Amicia and Hugo to flee from the army of Count Victor de Arles. The soldiers have positioned themselves on a narrow path, which can be represented as a matrix of dimensions . Furthermore, we know that there are a total of soldiers on this path.
Task
Amicia and Hugo define the danger of a configuration as the number of soldier groups in it. More formally, if we consider a binary matrix, where we have in the positions where a soldier exists. We say that two cells are connected if they both have value and they share an edge. Note that this relation is transitive, meaning that if two cells and are connected and cells and are connected, than and are also considered connected. A connected component is a maximal subset of connected cells with value . The danger is the number of connected components in this matrix.
Your task is to help the two protagonists find the expected value of the danger, considering all possible configurations. Each configuration is considered equiprobable. In this case, the expected value can be defined as the average number of connected components across all possible configurations.
Implementation
You have to implement the following functions:
void prec(int subtask_id)
int solve(int n, int k)
The first function will be called once at the beginning of the grader. You can use it for preprocessing.
The second function should return the expected danger, given the and parameters, modulo . Formally, let . It can be shown that the answer can be expressed as an irreducible fraction , where and are integers and . Return the integer equal to . In other words, return such an integer that and .
The second function will be called times. This means there are multiple testcases in the input!
Do not forget to include the header file "kor.h", otherwise you will get compile error!
Constraints
| # | Points | Constraints |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | |
| 2 | 5 | |
| 3 | 5 | |
| 4 | 15 | |
| 5 | 10 | |
| 6 | 15 | |
| 7 | 40 | No additional constraints. |
Example 1
input
2
6
2 2
5 10
2000 3
2000 5
100 32
150 278
output
332748119
1
518205646
742082393
368118258
937239298
Explanation
Note that the grader should be provided with the subtask of the test, the number of testcases and the values for each testcase.
For the first testcase of the first sample, the possible configurations are shown below:
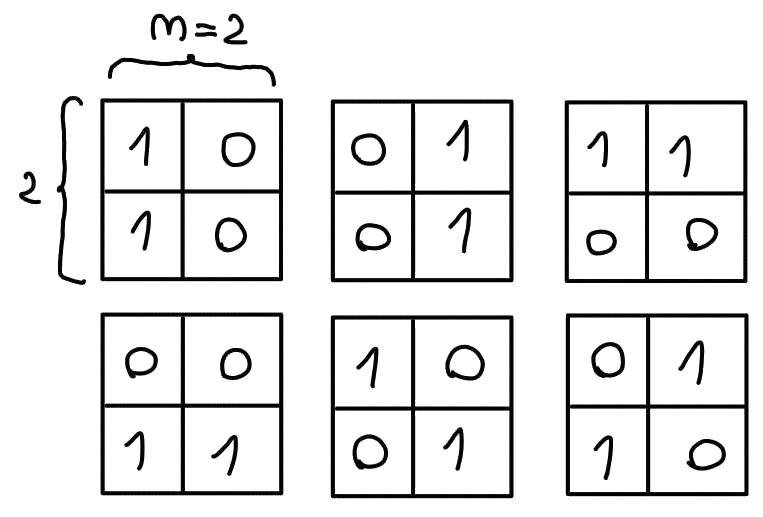
There is a total of configurations, of which have a single component. The answer is thus
Example 2
input
7
8
100000000 0
100000000 1
100000000 2
100000000 3
5219873 192
853875838 238
43782384 1500
58123292 180000
output
0
1
268791198
806373591
782159797
435727907
712321002
257644694