When people ask me, Flaviu, why I am such a die-hard fan of LucaLucaM, I often choose to quote a conversation I had with him nearly a year ago.
- Luca, why did you use HLD for this problem when it was just an Euler's Tour?
- Well, it was too boring with Euler's Tour, and I had two more hours in the contest, so I decided to use HLD at least.
Task
You are given a tree consisting of nodes and bidirectional edges. You are also given a list of nodes , where each node in this list is of type . Each node of type is assigned a value. All other nodes are of type . You are given queries. For each query, a set of nodes is provided, guaranteeing that all nodes in this set are of type . For each query, the nodes in the set have the signal initially. From then on, each second, any node of type will transmit the signal to all adjacent nodes, regardless of their type, and those of type will transmit the signal each second only to those adjacent with the same value or of type . This operation ends when there is no node left that does not have a signal and can receive it in the next second. You need to display for each query what is the maximum number of nodes that have the signal at the end.
Input data
The first line contains a natural number , the number of nodes.
Each of the following lines contains a pair of natural numbers and separated by spaces, indicating that there is an edge between nodes and .
The next line contains a natural number , the number of nodes of type .
The following lines contain pairs of two natural numbers, and , indicating that node is of type and has the value .
The following line contains a natural number , the number of queries.
The following lines contain a natural number , representing the number of nodes that initially have the signal in query , followed by numbers that represent the nodes that initially have the signal.
Output data
You will print the answers for each of the queries, in order, each on a new line.
Constraints and clarifications
- ;
- ;
- ;
- Let denote the cardinality of the set of nodes corresponding to query . Then, .
- Due to the very large input set, it is recommended to use fastio.
- For test cases worth points: all nodes on even levels are of type ;
- For other test cases worth points: ;
- For other test cases worth points: the tree is a chain of the form .
Example 1
stdin
10
1 2
1 3
2 7
2 8
3 4
3 5
3 6
8 9
4 10
7
2 3
3 6
7 3
9 4
4 4
5 6
6 7
4
3 1 8 10
1 10
1 1
1 8
stdout
9
2
7
7
Explanation
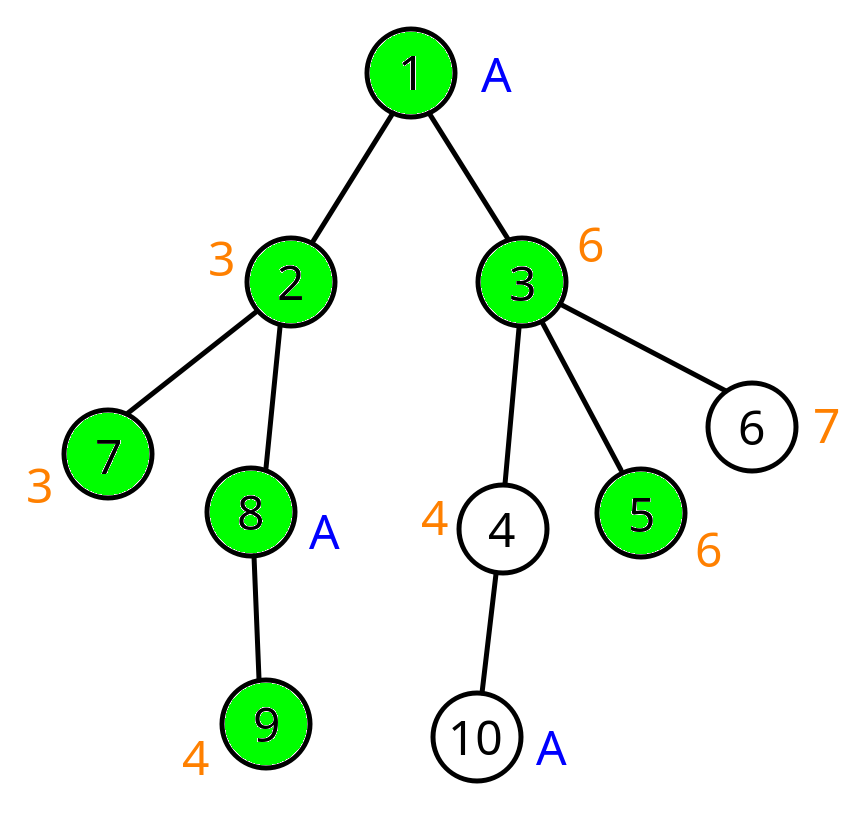
We will color the nodes with signal in green. In the first query, the tree looks like this:
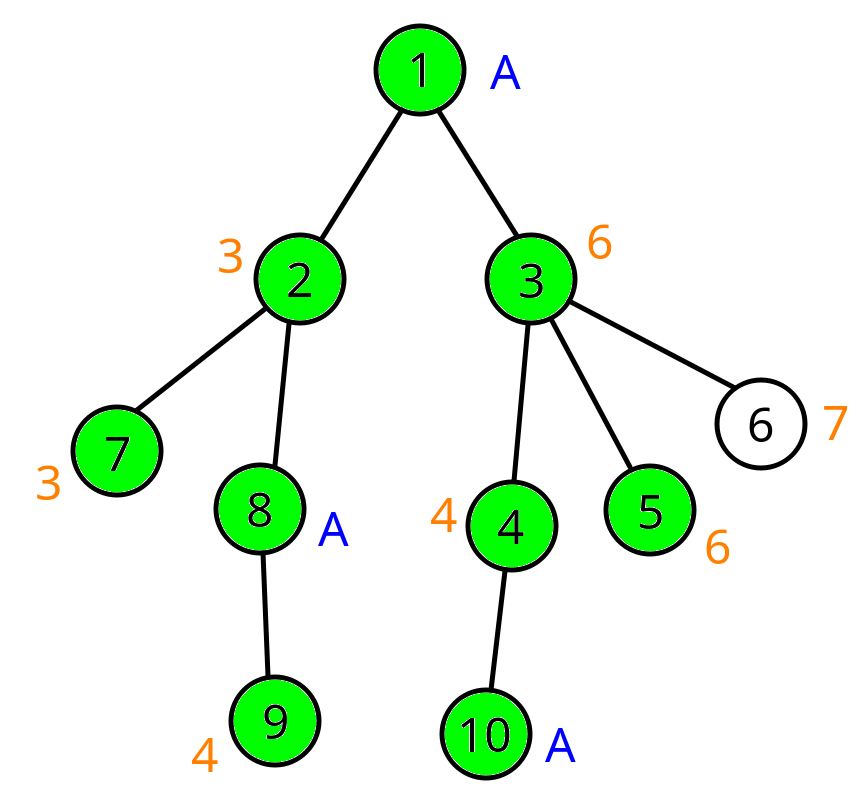
In the second query, the tree looks like this:
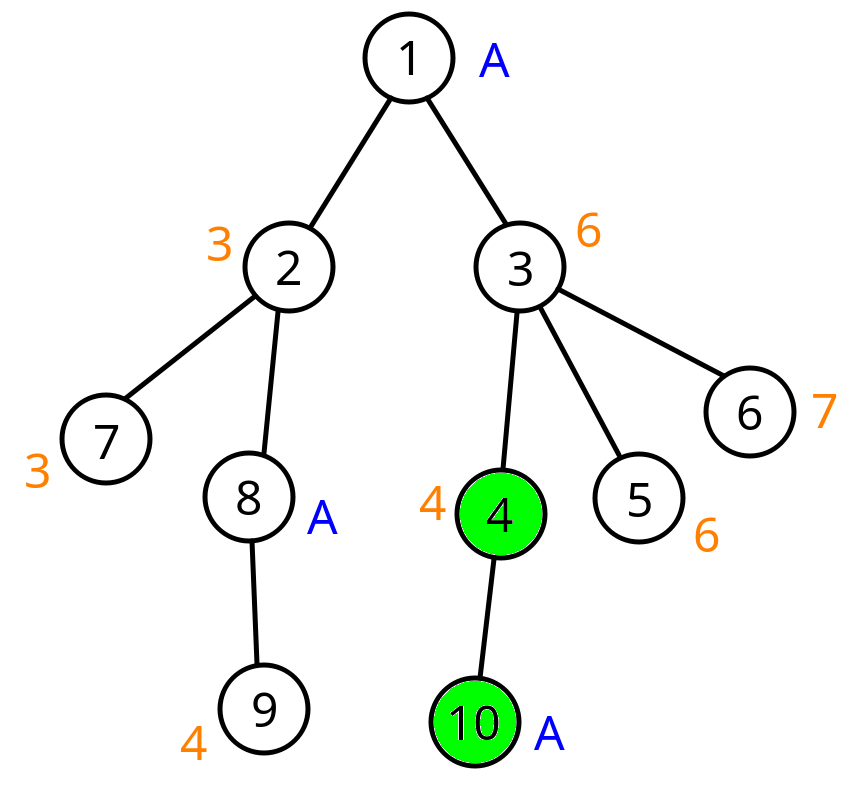
In the third and fourth queries, the tree looks like this: