Note: during the contest, the time limit was raised to 1.5 seconds, but we have brought it back down to 0.6 seconds to encourage solutions of the utmost efficiency.
Bobi has discovered a fun data structure, namely the heap. More specifically, a heap is a tree-like data structure in which each node has a certain value and at most two direct children, namely the left child and the right child. Heaps can be of two types:
- max-heap, where the value of each node is greater than the values of its direct children. As a result, the root of a max-heap contains the maximum value from the heap.
- min-heap, where the value of each node is less than the values of its direct children. As a result, the root of a min-heap contains the minimum value from the heap.
For example, here is a heap containing numbers :
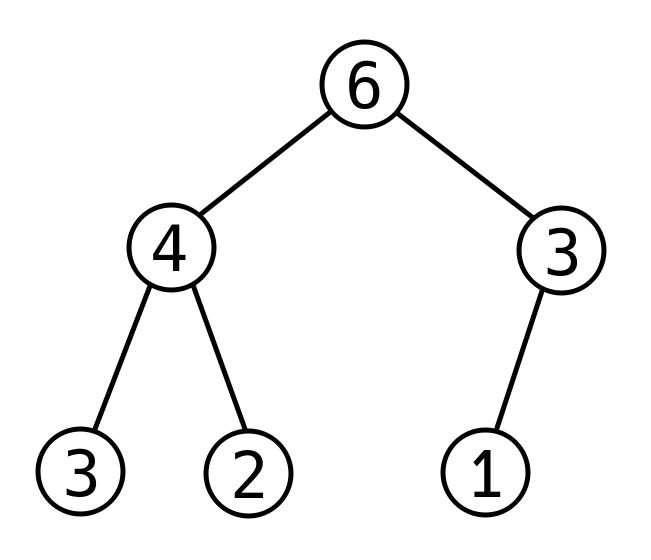
Bobi is playing with the first type of heap mentioned above by initially adding numbers to it. He wants to perform operations of the following types:
- - Bobi inserts the value into the heap;
- - Bobi deletes one occurrence of the value from the heap. If it doesn't exist, the heap remains unchanged;
- - Bobi extracts the largest values from the heap, then decreases each of them by , and inserts them back into the heap. If , all values in the heap will be extracted.
Task
Help Bobi obtain the heap after performing all the operations and print the numbers from the final heap in descending order.
Input data
The first line contains the numbers and .
The second line contains the numbers, in descending order, representing the initial heap.
The following lines contain the operations, as described in the statement.
Output data
Print the final heap on a single line, with the numbers separated by a single space, in descending order.
Constraints and clarifications
- ;
- ;
- ;
- ;
- The initial elements of the heap are given in descending order;
- For points: ;
- For another points: ;
- For another points: ;
- Fast input/output is recommended.
Example 1
stdin
8 1
8 8 8 8 5 4 4 1
3 5 2
stdout
6 6 6 6 4 4 3 1
Explanation
The largest elements are , , , , and . By decreasing them by and inserting them back into the heap, we get .
Example 2
stdin
0 7
1 4
1 5
1 7
3 2 4
2 3
1 6
1 7
stdout
7 6 4 1
Explanation
Initially, the heap is empty.
After the first operation, is inserted. The heap is: .
After the second operation, is inserted. The heap is: .
After the third operation, is inserted. The heap is: .
After the fourth operation, the largest numbers, and , are extracted. By decreasing them by and inserting them back into the heap, we get .
After the fifth operation, is deleted. The heap is: .
After the sixth operation, is inserted. The heap is: .
After the seventh operation, is inserted. The heap is: .