Hu’s Garden can be visualized as a Cartesian coordinate system. He wants to choose a triangle from his garden in which to plant more flowers. He has already decided on two of the lines that form the triangle, and you must help him find the third one, knowing that he wants to plant exactly flowers and that flowers are planted at every point with integer coordinates inside and on the boundary of the triangle, and only at those locations. He also wants flowers to be planted at the vertices of the triangle.
Task
Formally, you are given a natural number , which represents the size of a plane, and lines defined by equations of the form , where , , are natural numbers and . You must find points (with integer coordinates) in the plane that form a triangle such that it contains lattice points (with integer coordinates) on its boundary or in its interior, and among the lines determined by the vertices, of them are the given ones.
Input Data
On the first line you will read, in order, numbers: , , , , , , , ; where is the size of the plane, is the number of flowers inside the triangle, , and are the parameters of the first line, and , and are the parameters of the second line.
Output Data
If a solution exists, you must output numbers separated by a space: , , , , and , representing the coordinates of the points. Otherwise, you must output .
Constraints
- The plane is considered to have vertices at the points , , and .
- It is guaranteed that the given lines intersect at a single point and that this point is a lattice point with coordinates between and .
- The triangle must have all vertices distinct in order to be considered valid.
- If multiple solutions exist, any of them may be output.
| # | Points | Restrictions |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | |
| 2 | 20 | |
| 3 | 30 | |
| 4 | 40 | No additional constraints |
Example 1
stdin
10 6 1 5 1 0 6 1
stdout
1 6 0 5 5 6
Explanation
In the first example, a valid solution is , , . The first line is the one colored orange, the second one is colored blue, and in green we have the third line determined by two of the points. In red we have the lattice points inside and on the sides of the resulting triangle.
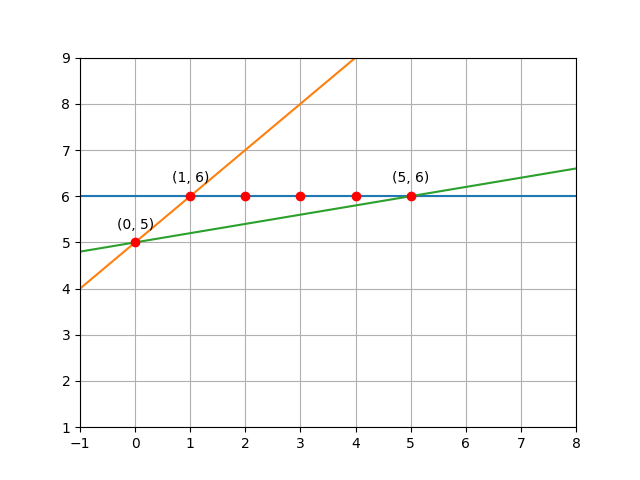
Another valid solution, defined by the points , and , can be seen in the image below. The triangle defined by the lines also contains lattice points.
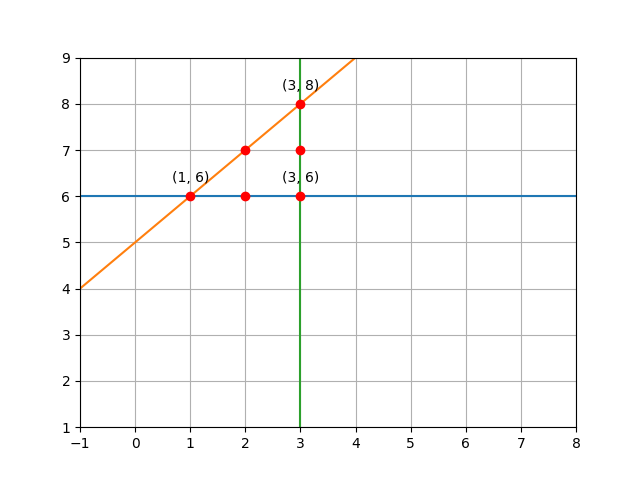
Example 2
stdin
80 52 -1 80 8 1 0 2
stdout
16 8 8 9 34 17